6. Machine learning for understanding urban heat island
Machine learning for understanding urban heat island
Background
Urban heat island (UHI), a phenomenon that an urban area has higher air temperature than a rural area, has been an increasing public concern in the time of climate change since it imposes impressing challenges to the health of inhabitants and resilience of many societal systems. A viable mitigation measure that attracted extensive research interest is to have more vegetation in cities. The presence of vegetation affects urban climate as a result of multiple mechanisms, for instance, the evapotranspiration effect, shading effect, aerodynamic resistance to wind and heat transfer, etc.
These mechanisms take place at different scales in time and space. To better understand the impact of vegetation on urban heat mitigation, machine learning models can be employed to gain insight into the complex dependence of various influencing factors, ultimately providing a powerful tool for city planners.
Keywords
Machine learning, vegetation, urban heat island, heat mitigation
Labels
Semester Project & Master Thesis, (2022-2023)
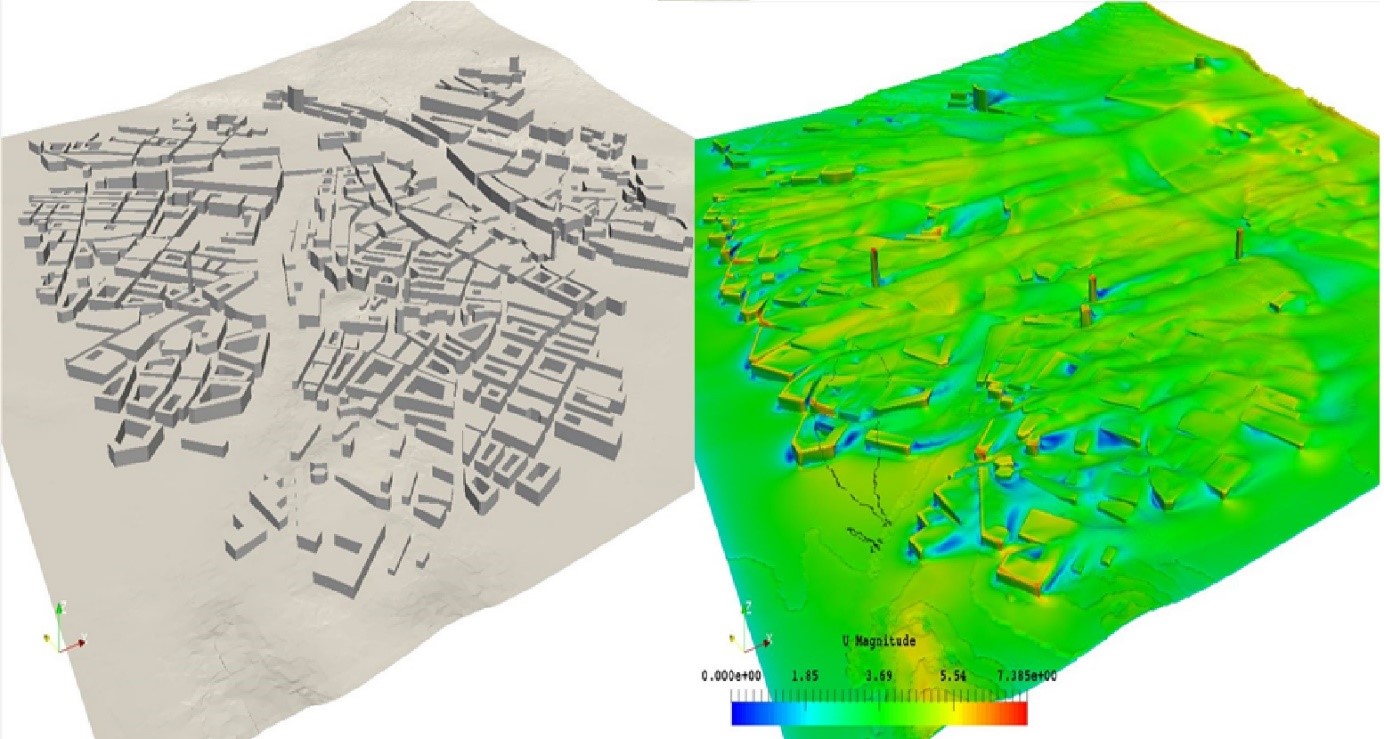
Description
The ultimate cooling benefits that plants and trees may bring to cities depend on a series of connected factors, such as plant cover, the presence of ventilation corridors, urban textiles, etc.
Machine learning can be a powerful tool for better understanding the contribution of plant and urban trees in heat mitigation. An effective machine learning model for assessing the city-scale cooling benefit of the plant at high spatio-temporal resolution will be proposed. Land cover, urban morphology, and social-economic information will be encoded to be key explanatory factors. The model will ultimately facilitate decision-makers to plan heat mitigation strategies.
Goals and tasks
1. Analyze land cover, urban morphology, and meteorological data
2. Establish a deep-learning model
3. Propose heat mitigation initiatives using the deep-learning model
Contact details
Please contact Dr. Yongling Zhao () for further information