Rain droplets in the built environment
Rain is the main source of moisture affecting the performance and durability of the built environment.
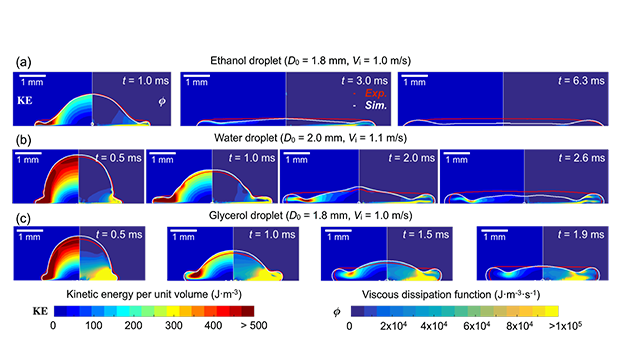
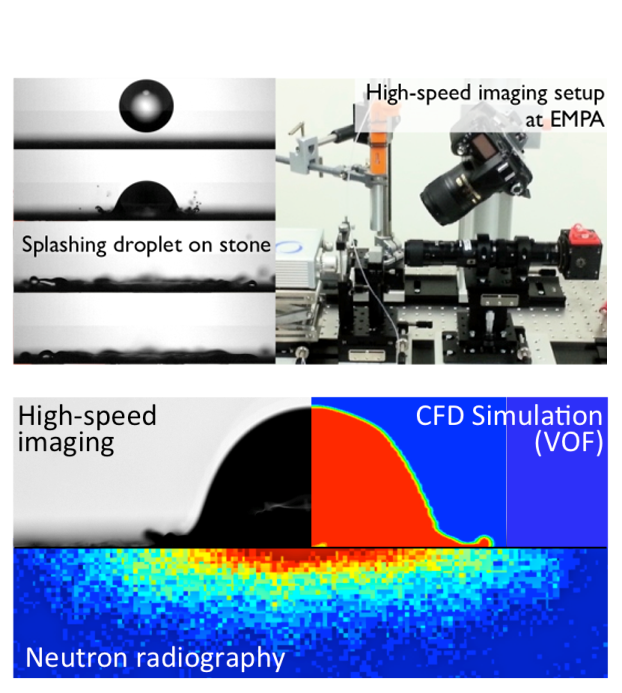
Droplet impact on surfaces is an important phenomenon in various engineering applications. Droplet impact during wind-driven rain governs the wetting of building facades, a main factor of moisture damage of materials. To capture the phenomena of raindrop impact on porous materials, various imaging techniques and numerical simulation methods are used such as high-speed imaging, neutron and X-ray radiography, CFD and volume of fluid (VOF).
Film forming and runoff
Models for film forming and runoff as well as evaporation have been developed, based on the compressible Navier-Stokes equation and solved with the finite volume method. Numerical results have been validated against existing experimental results for film runoff for inclined plates.
Wind-driven rain
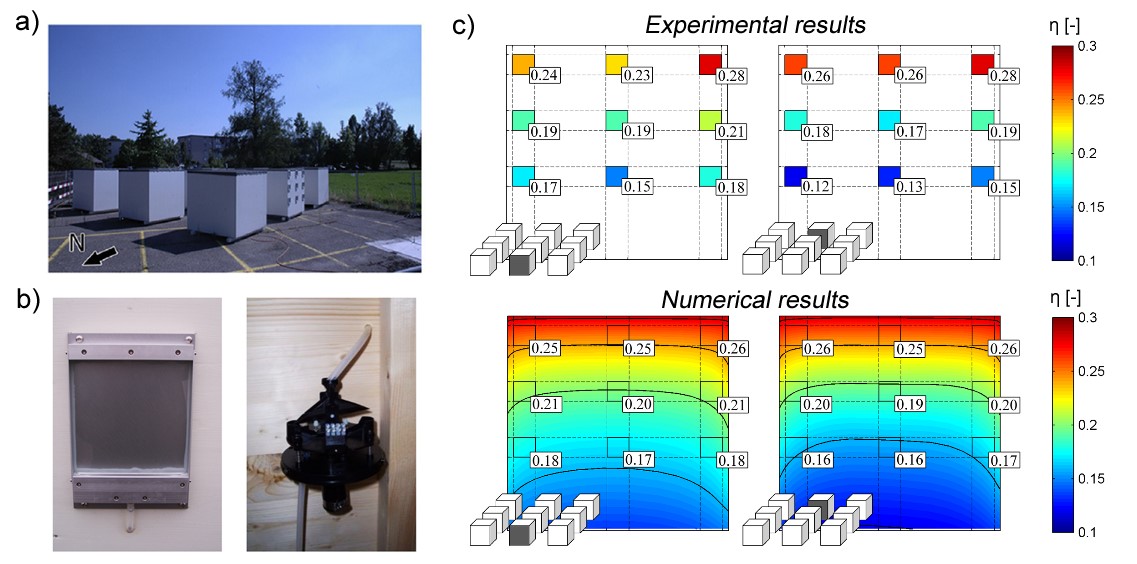
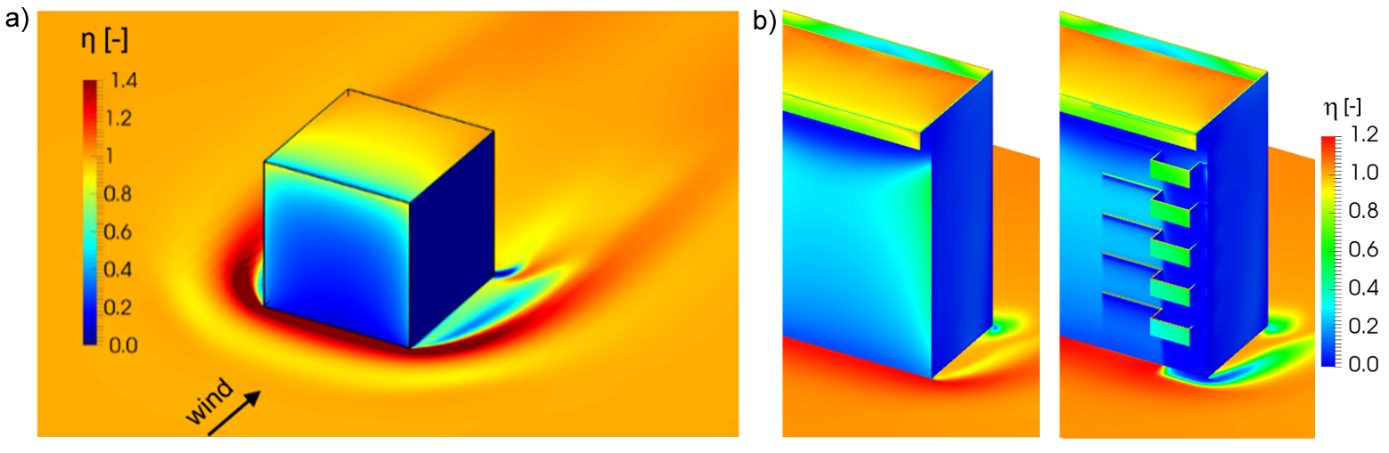
Accurate determination of surface wetting distribution is the first step towards moisture studies on building envelopes. Droplet impingement on façades is influenced by the complex wind flow patterns around the buildings, façade details on buildings and atmospheric conditions, i.e. rainfall intensity, wind speed, wind direction. CFD simulations can be used to obtain accurate and detailed spatial and temporal distribution of wind-driven rain. Turbulent dispersion of raindrops has been modeled using an Eulerian multiphase model for estimation of wind-driven rain. Field experiments are performed to validate the numerical modelin multiple geometries representing urban neighborhoods.
The solver developed for the finite volume code OpenFOAM, windDrivenRainFoam, is made available in the Downloads section.
The datasets of rain events obtained during field measurements are available online for download and are intended for model development and validation. Downloads
Publications
Derome D, Kubilay A, Defraeye T, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2017. Ten questions concerning modeling of wind-driven rain in the built environment. Building and Environment; 114:495–506.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Carmeliet J. 2017. Analysis of time-resolved wind-driven rain on an array of low-rise cubic buildings using large eddy simulation and an Eulerian multiphase model. Building and Environment; 114:68-81.
Kubilay A, Carmeliet J, Derome D. 2017. Computational fluid dynamics simulations of wind-driven rain on a mid-rise residential building with various types of facade details. Journal of Building Performance Simulation; 10(2):125-143.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2015. Wind-driven rain on two parallel wide buildings: field measurements and CFD simulations. Journal of Wind Engineering & Industrial Aerodynamics; 146:11-28.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2015. Numerical modeling of turbulent dispersion for wind-driven rain on building facades. Environmental Fluid Mechanics; 15(1):109-133.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2014. Numerical simulations of wind-driven rain on an array of low-rise cubic buildings and validation by field measurements. Building and Environment; 81:283-295.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2014. High-resolution field measurements of wind-driven rain on an array of low-rise cubic buildings. Building and Environment; 78:1-13.
Kubilay A, Derome D, Blocken B, Carmeliet J. 2013. CFD simulation and validation of wind-driven rain on a building facade with an Eulerian multiphase model. Building and Environment; 61:69-81.